Switchgear & Controlgear:
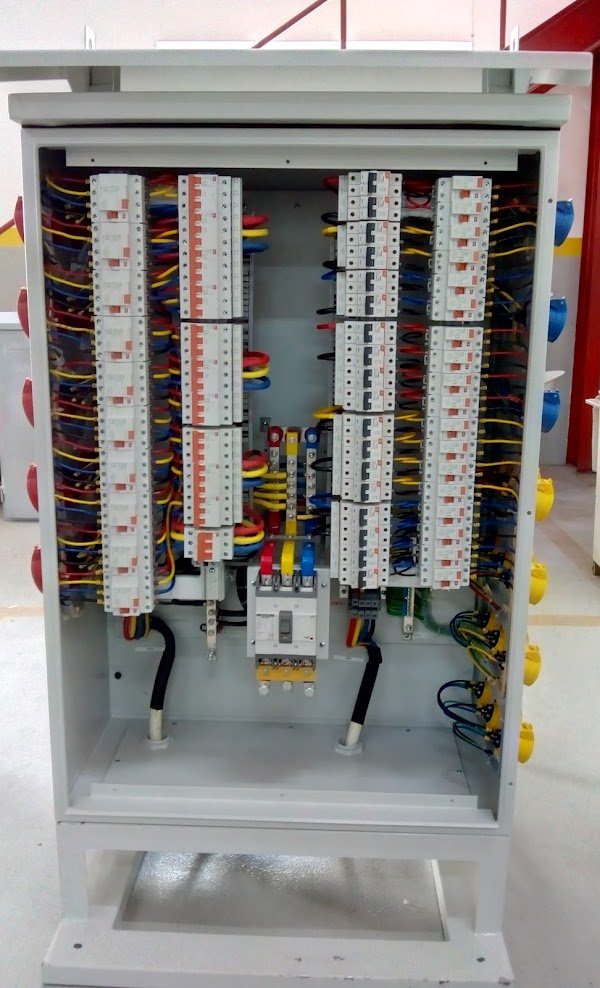
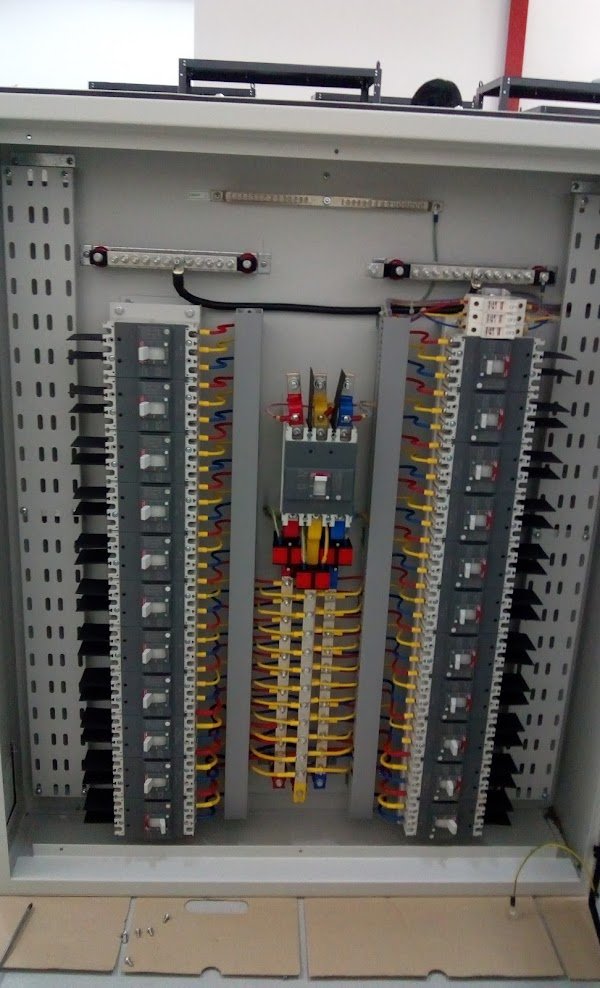
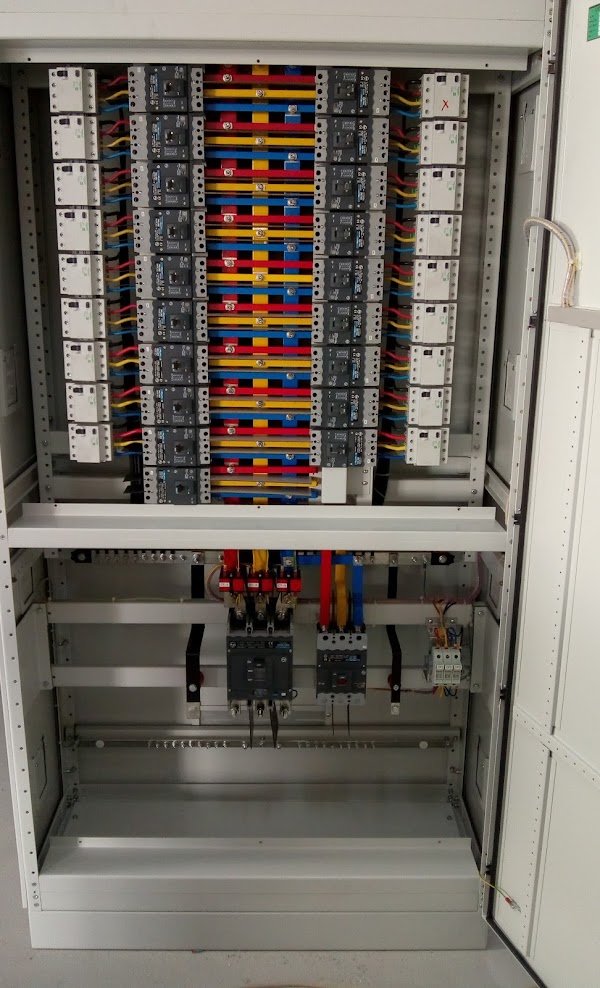
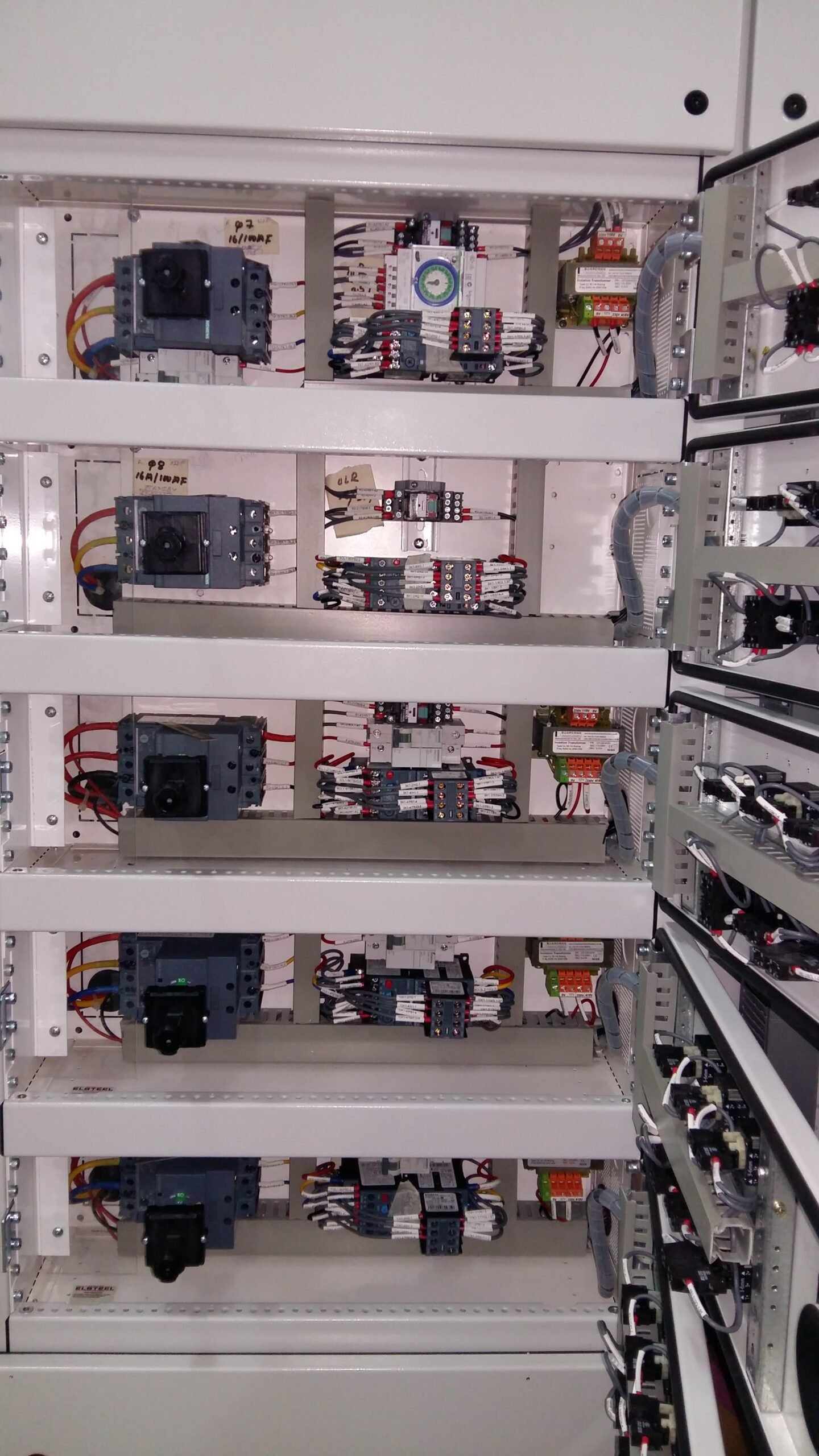
We are a leading manufacturer of low voltage switchgear and Control gear with form separation, Form-2…, Form-3… and -Form-4…. each individually designed to cater for exact customer requirements as per the IEC 61439 standard and approved by EWA. Our switchgears are being used for EWA network, commercial buildings, residential buildings, Industries, Educational & health sector and other Ministries.
Main Distribution
Board (MDB):
Components:
Incoming Power Supply:
- Main Circuit Breaker (ACB / MCCB): Protects the entire electrical system by disconnecting power in the event of a fault or overload.
- Busbars: Copper (Purity 99.98%) strips that conduct electricity from the incoming power supply to various circuits within the board. Busbar size based on the load.
Outgoing Circuits:
- Circuit Breakers (ACB/MCCB): Individual protective devices for each outgoing circuit, designed to protect against overloads and short circuits.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs): Provide protection against earth faults, ensuring safety by disconnecting the circuit if a leakage current is detected.
- Surge Protection Devices: Protect the electrical system from voltage spikes, often caused by lightning or switching surges.
Metering and Monitoring:
- Energy Meters (Provisional): Measure the consumption of electrical power, which can be used for billing or monitoring purposes.
- Voltage and Current Indicators: Provide visual feedback on the status of the electrical supply and distribution.
Enclosure:
- Metal or Insulated Enclosure (GRP): Protects the internal components from environmental factors and unauthorized access, typically rated for specific IP standards to ensure safety.
- Metal enclosure made from 2mm for structure and 1mm doors and cover from.
- Separate compartment for incoming & outgoing feeders.
- All the doors are provided with hinges, locks and gasket.
- Powder coated with the RAL color 7035 /7032. Any other color on request.
- Available in Form-2…,3… and Form-4…
Earthing and Bonding:
- Earthing Busbar: Ensures proper grounding of the electrical system, providing a path for fault currents and enhancing safety.
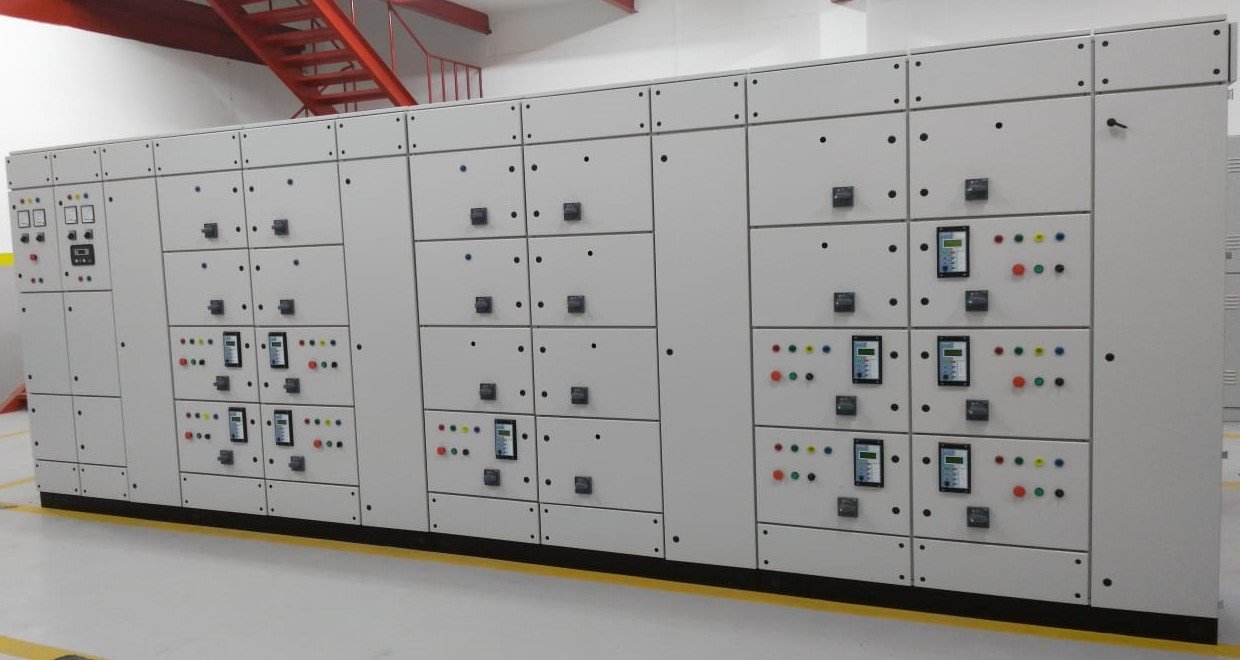
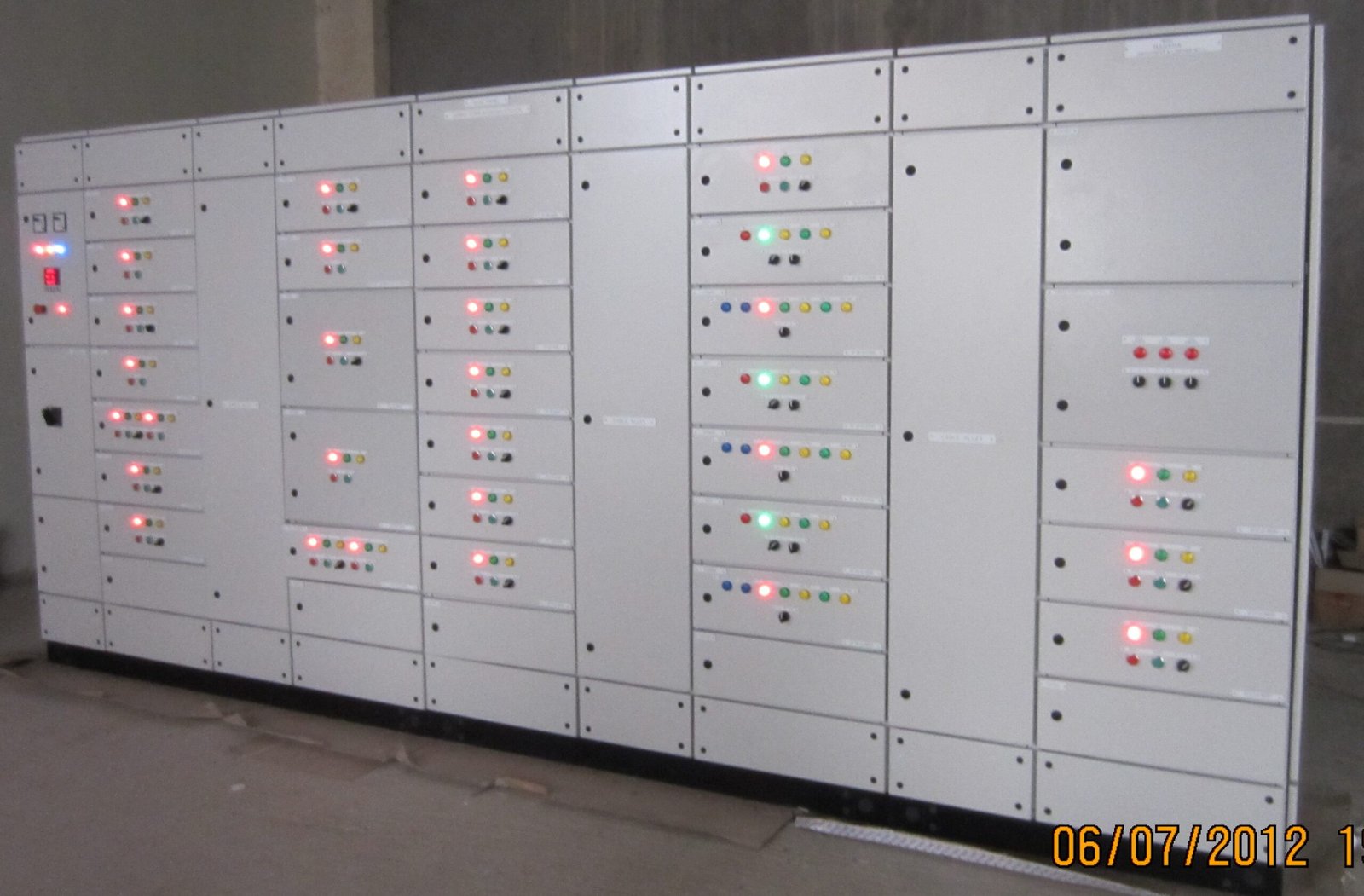



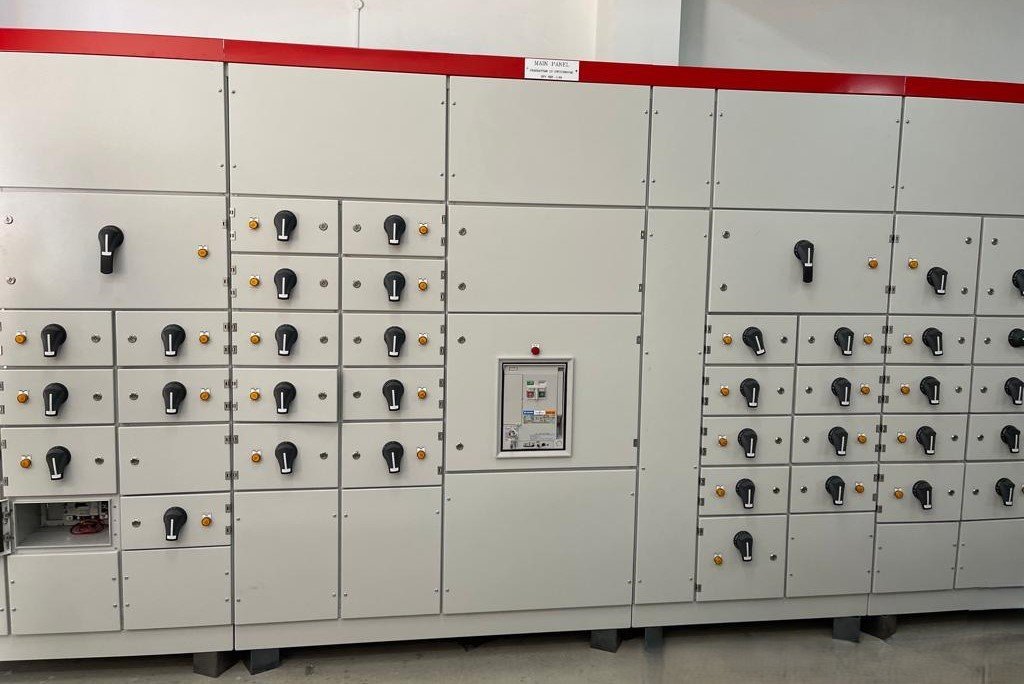
Functionality:
- Power Distribution: The MDB distributes electrical power from the main supply to various sub-distribution boards or directly to end-use equipment such as lighting, HVAC systems, and machinery.
- Protection: Provides protection for the entire electrical system through circuit breakers and other protective devices, preventing damage from overloads, short circuits, and earth faults.
- Control: Enables manual control of electrical power to various sections of the facility, allowing for maintenance, troubleshooting, and energy management.
- Monitoring: Allows for real-time monitoring of electrical parameters, aiding in energy management, fault diagnosis, and ensuring compliance with electrical standards.
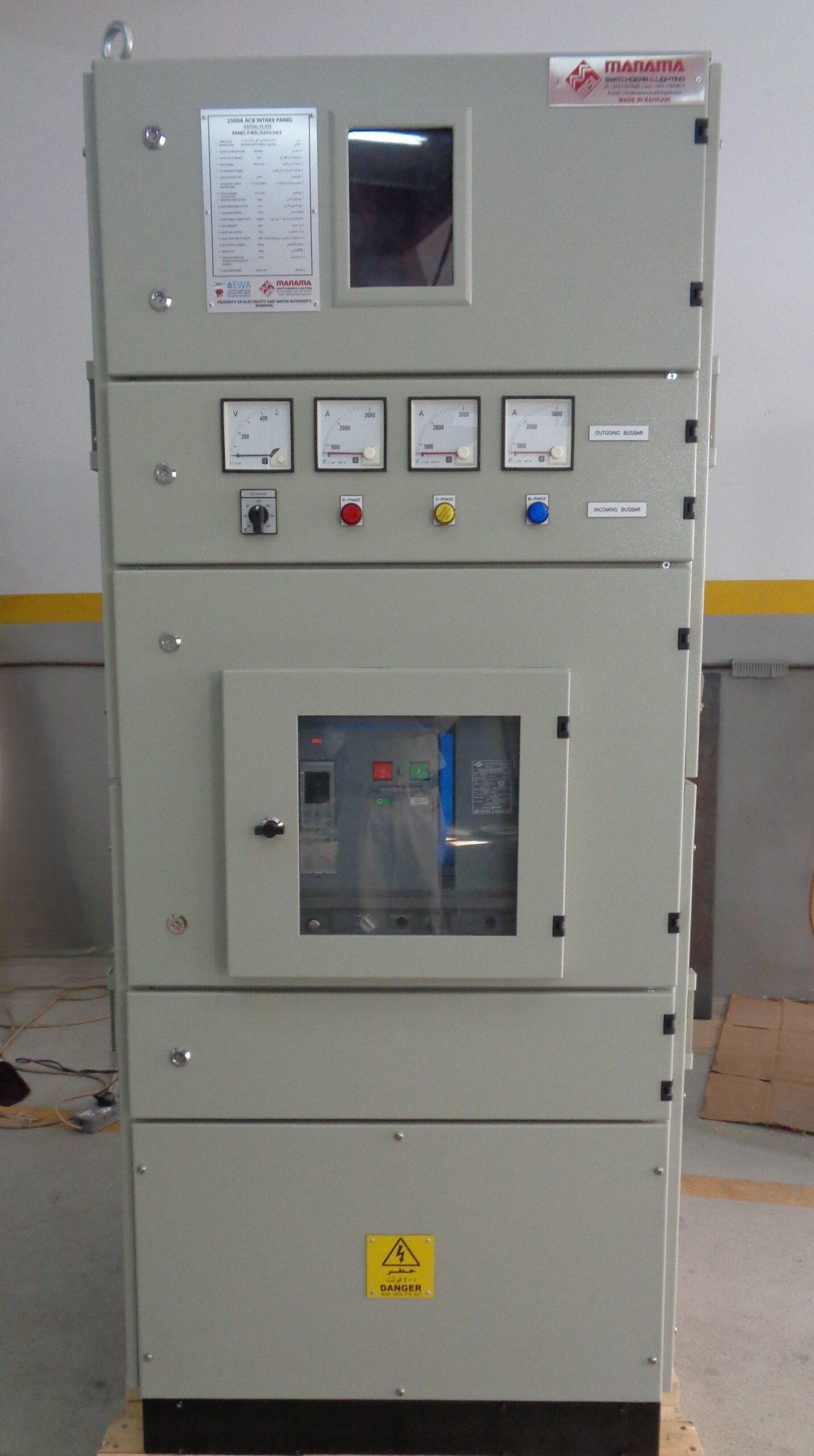


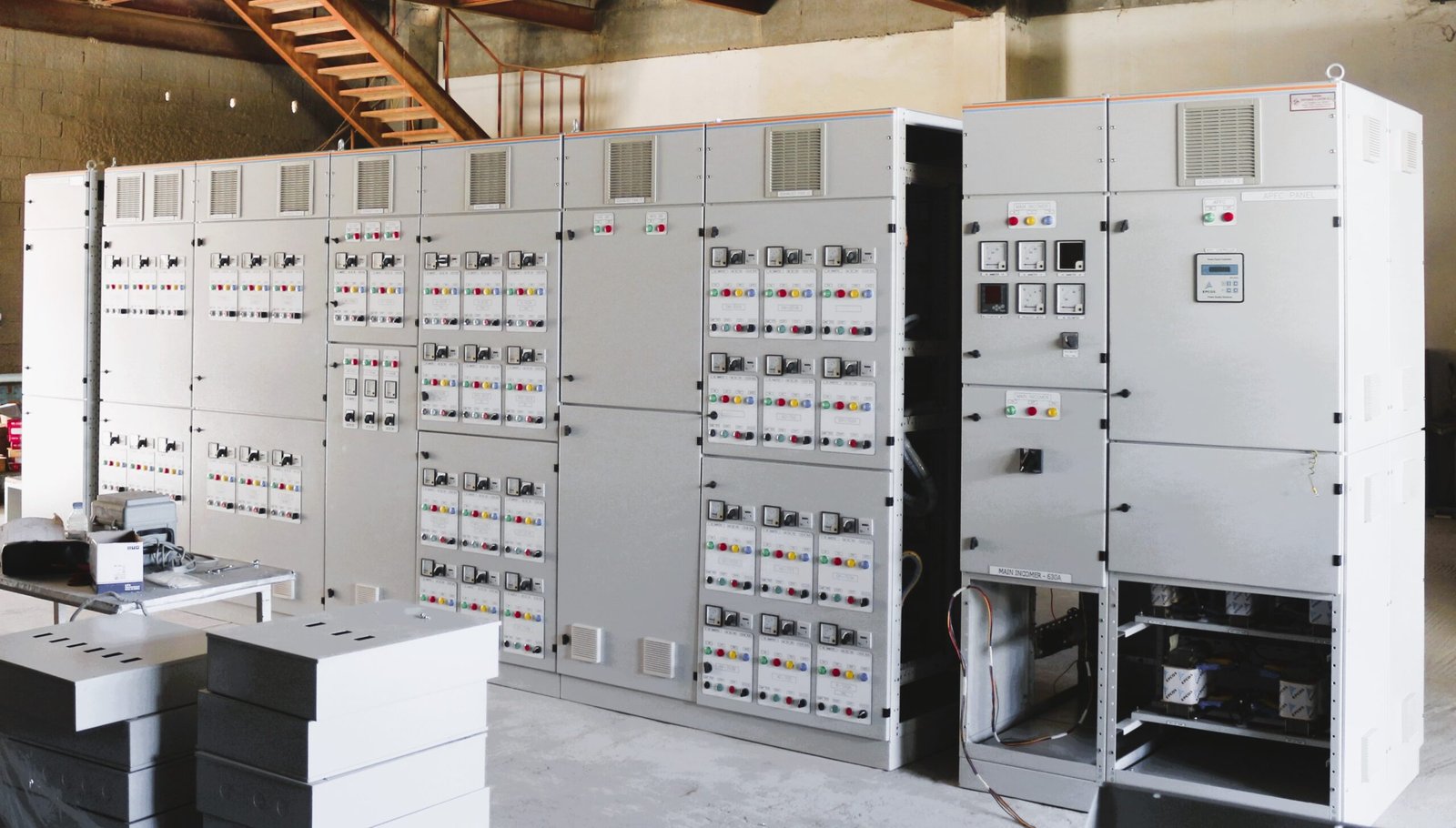
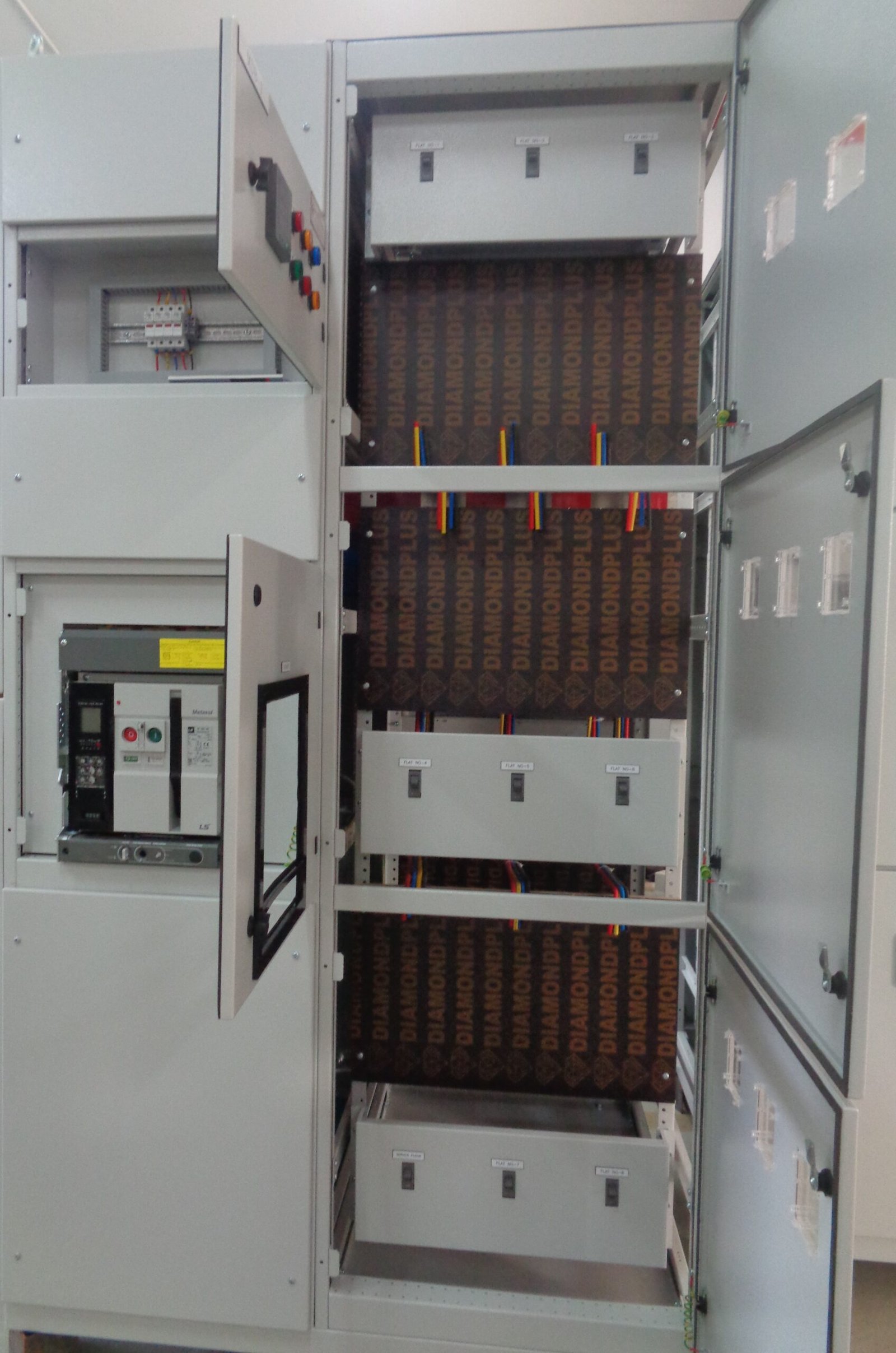
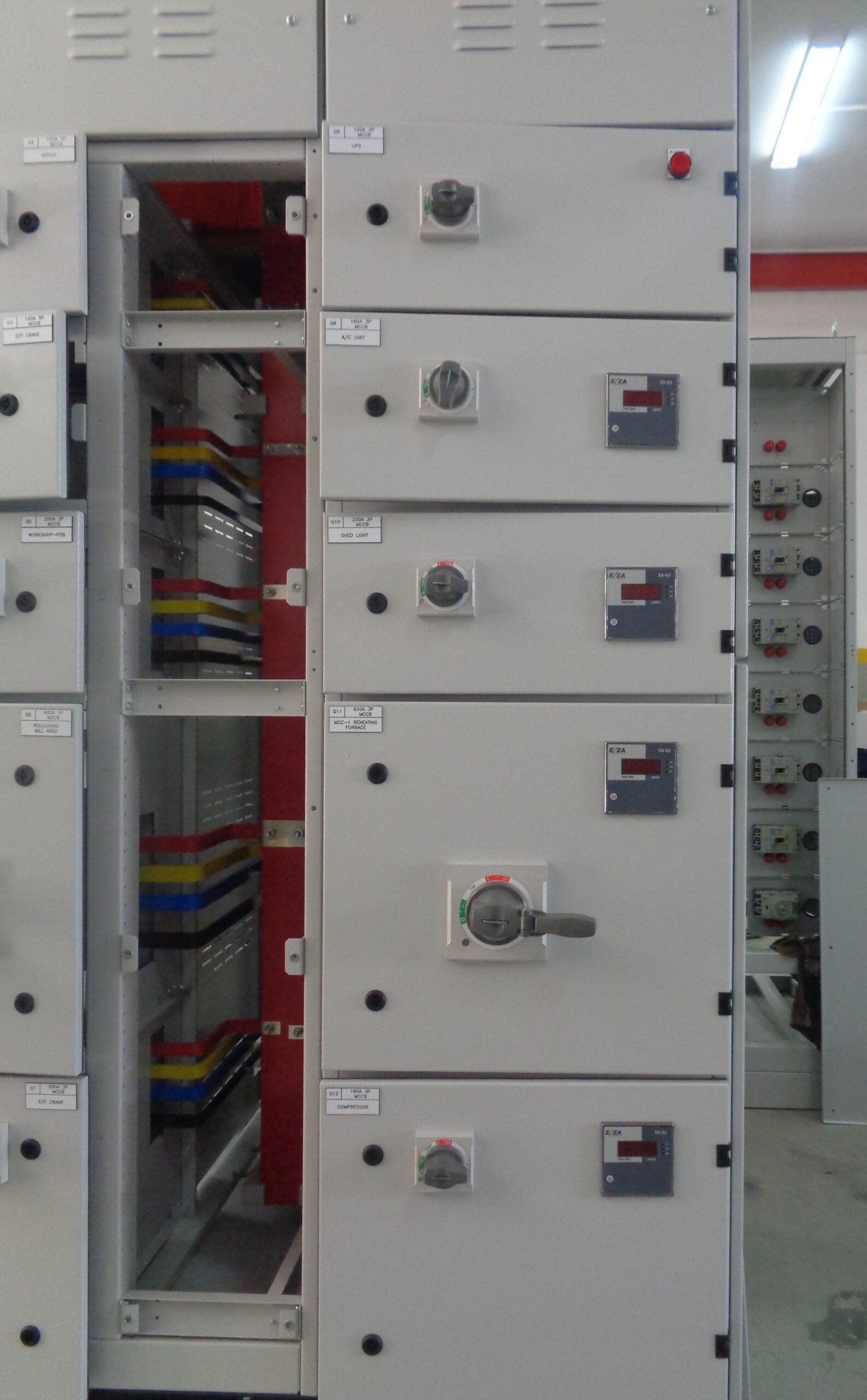
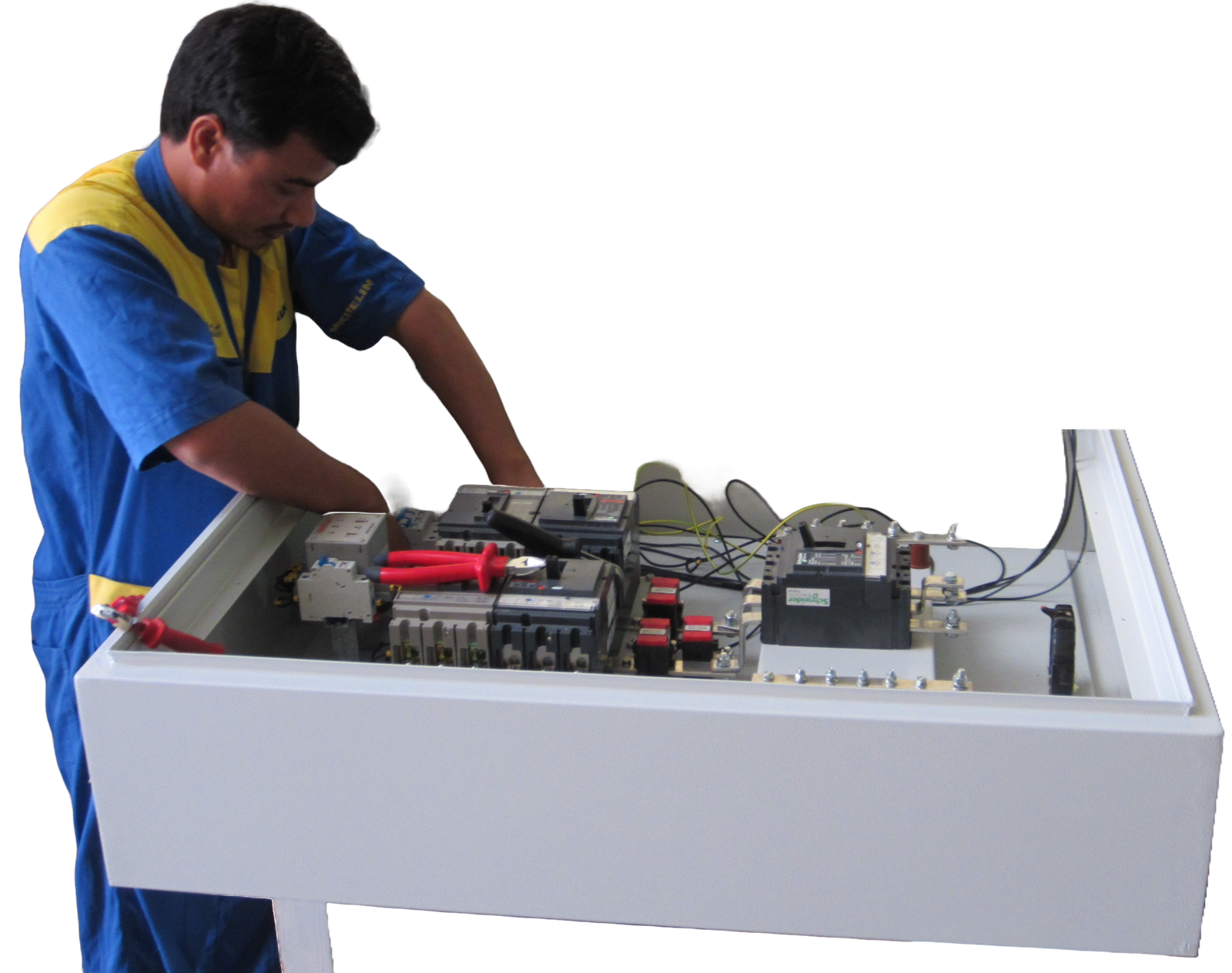
ACB Intek Panel (2500A, 1600A & 800A):
These ACB Intek panels are being used in Electricity Distribution Directorate (EDD) network.
All the EDD substations are installed with these type of ACB Intek Panels. The Ampere rating depends upon the transformer size. The MDBs in consumer’s electrical room are being connected through these panels.
Metering Panel:
This type of panel is being installed in Landlord’s electrical room of multi-story building. This panel is having provision for installing the KWH (Energy) meters provided by the EWA / EDD. Each separate KWH meter is being connected to the individual flat of the building.
Customized Size of the panel depends upon the Load, design, of out goings and size of the electrical room.





Sub Main Distribution
Board (SMDB):
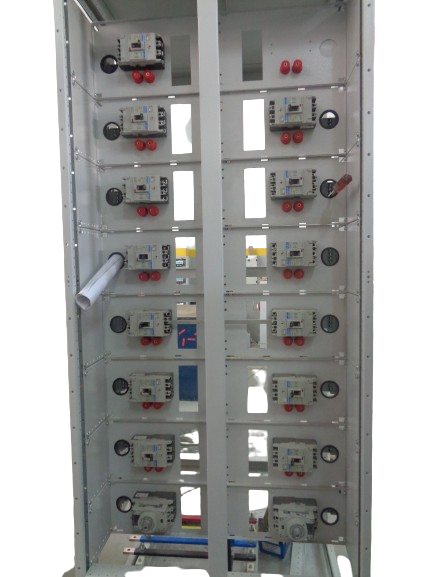
Components:
Incoming Circuit:
- Main Circuit Breaker: Provides protection and isolation for the entire SMDB, usually connected to the MDB or another upstream distribution board.
- Busbars: Copper (Purity 99.98%) strips that conduct electricity from the incoming power supply to various circuits within the SMDB. Busbar size based on the load.
Outgoing Circuits:
- Circuit Breakers: Protect each outgoing circuit, similar to those found in the MDB, designed to prevent overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs) or Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs): Optional protection devices that safeguard against earth faults.
Monitoring Devices:
- Meters and Indicators: May include energy meters, voltage and current indicators, to monitor power consumption and system health at the SMDB level.
- Meters and Indicators: May include energy meters, voltage and current indicators, to monitor power consumption and system health at the SMDB level.
Enclosure:
- Protective Housing: Often made of metal, designed to protect the internal components from environmental factors and unauthorized access, with appropriate IP ratings.
- Metal enclosure made from 2mm for structure and 1mm doors and cover from.
- All the doors are provided with hinges, locks and gasket.
- Powder coated with the RAL color 7035 /7032. Any other color on request.
Earthing System:
- Earthing Busbar: Ensures all components within the SMDB are properly grounded for safety.
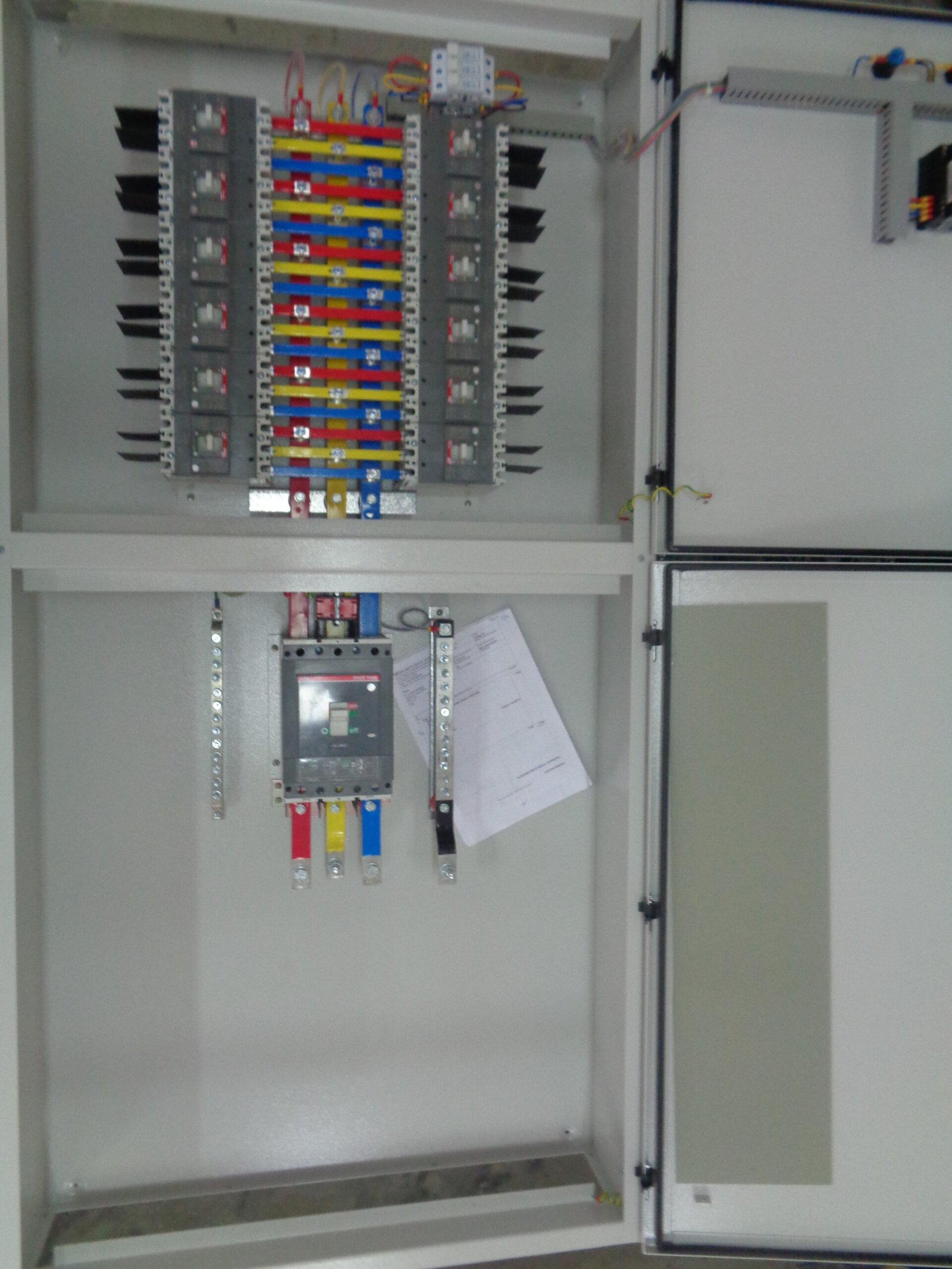

Functionality:
- Intermediate Power Distribution: The SMDB acts as a distribution point between the MDB and final distribution points (like lighting panels, socket outlets, or specialized equipment), enabling efficient power distribution to various sections or floors of a building.
- Enhanced Protection: Provides additional layers of protection by segmenting the electrical distribution into smaller, more manageable sections. Each section can be isolated or protected independently.
- Load Management: Allows for better load management and distribution, which is particularly important in large facilities with diverse and fluctuating power demands.
- System Flexibility: Facilitates expansion and modification of the electrical system, making it easier to add new circuits or redistribute loads without affecting the entire network.
Applications:
- Commercial Buildings: In multi-story buildings, SMDBs are often installed on each floor to manage power distribution from the MDB to specific areas or rooms.
- Industrial Plants: Used to distribute power to different sections of the facility, such as production areas, administrative offices, or specific machinery.
- Large Residential Complexes: SMDBs may be used to distribute power from the main board to different wings, floors, or sections of the complex.
- Infrastructure Projects: In large infrastructure projects like airports, hospitals, or shopping malls, SMDBs help manage the distribution of power to various zones or departments.
Importance:
- Localized Control: Provides localized control and monitoring of electrical power, making it easier to manage, maintain, and troubleshoot specific sections of a facility.
- Safety and Reliability: Enhances the safety and reliability of the electrical distribution system by preventing faults in one section from affecting the entire system.
- Efficiency: Improves the efficiency of power distribution by reducing energy losses and ensuring that power is delivered where it is needed most, with minimal disruption.
The SMDB is crucial in large and complex electrical systems, enabling effective power management and ensuring that power is distributed safely and efficiently across different areas or sections of a facility.
Specifications:
- Bus bars- copper purity 99.98% tinned 10micron coated, available from 100 to 800Amps. Capacity.
- Bus bar ratings. As per requirement 100 to 800Amps. Capacity.
- Neutral/earth bars are provided based on the size of load.
- Incomer – from 60 to 800Amps 3P + N.
- Outgoings as per requirements from 2-16 way load center assembly.
- Enclosure is provided with separate compartments for incoming and outgoing and metering.
- All the doors are provided with hinges, locks and gasket.
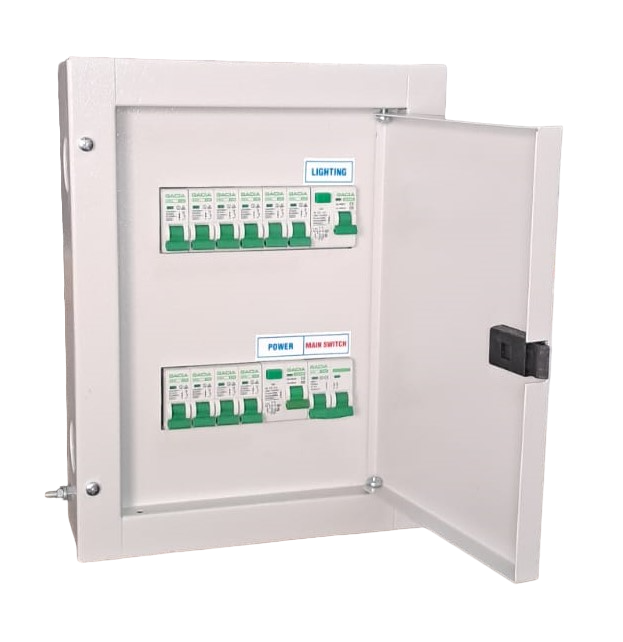
Distribution Board
(DB)
Components:
Incoming Supply:
- Main Switch: Controls the overall power supply to the distribution board, allowing for isolation of the entire board when needed.
- Busbars: Conduct electricity from the incoming supply to the circuit breakers, distributing power across different circuits.
Outgoing Circuits:
- Circuit Breakers or Fuses: Protect individual circuits by disconnecting them in the event of an overload, short circuit, or other electrical fault.
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs) or Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs): Provide additional protection by detecting earth faults and disconnecting the circuit if leakage currents are detected.
Enclosure:
- Protective Housing: Typically made of metal or plastic, the enclosure safeguards the internal components from external elements, dust, and unauthorized access, and is often rated according to IP standards for protection.
Earthing and Bonding:
- Earth Busbar: Ensures that all circuits and metal parts of the DB are properly grounded, enhancing safety by providing a path for fault currents.
Neutral Bar:
- Neutral Busbar: Provides a common return path for the electric current, ensuring that the electrical system operates safely and efficiently.
Functionality:
- Power Distribution: The DB divides the electrical power into subsidiary circuits, ensuring that power is delivered to various sections or devices within a building.
- Protection: Provides protection against electrical faults by using circuit breakers or fuses, which automatically disconnect the circuit in case of an overload, short circuit, or earth fault.
- Control: Allows for manual control of power to individual circuits, enabling maintenance, repairs, or isolation of specific areas without affecting the entire system.
- Monitoring: Some distribution boards may include metering devices or indicators to monitor power usage, helping in energy management and fault detection.
Applications:
- Residential Buildings: Distributes power to various circuits within a home, such as lighting, heating, and appliances.
- Commercial Buildings: Used in offices, retail spaces, and other commercial environments to manage power distribution to different areas or floors.
- Industrial Facilities: Distributes power to machinery, equipment, and lighting in manufacturing plants, warehouses, and other industrial settings.
- Small Infrastructure Projects: Used in smaller infrastructure projects, like schools, clinics, and community centers, to manage and distribute power effectively.
Importance:
- Safety: Ensures that electrical power is distributed safely, with built-in protection mechanisms to prevent electrical hazards.
- Convenience: Allows for easy control and management of power distribution, making it simple to isolate specific circuits for maintenance or troubleshooting.
- Efficiency: Helps in efficient power management by dividing the electrical load among various circuits, reducing the risk of overload and optimizing energy use.
The Distribution Board is an essential part of any electrical system, acting as the central point for managing and distributing electrical power to various circuits within a building or facility, ensuring both safety and reliability.
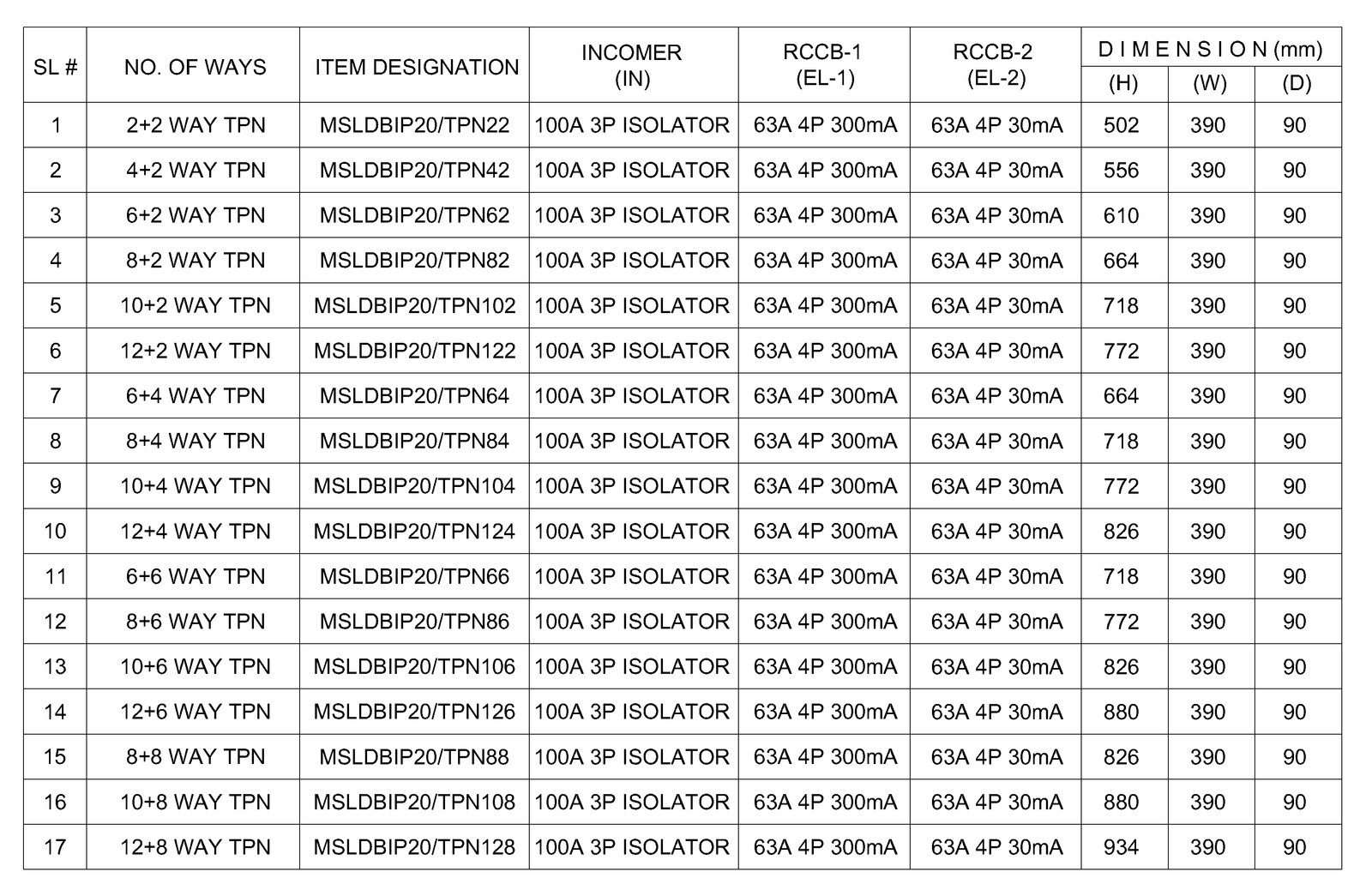
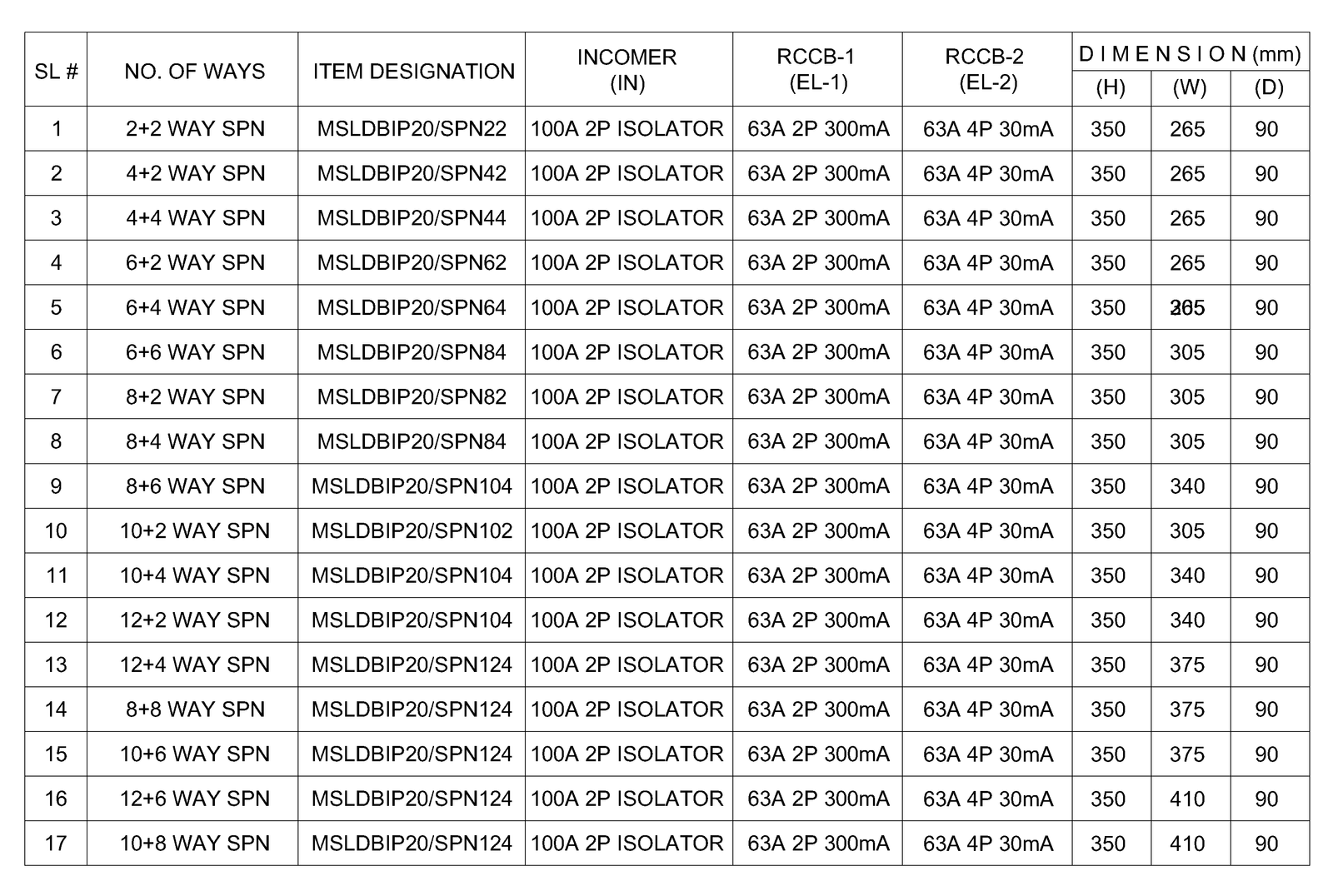
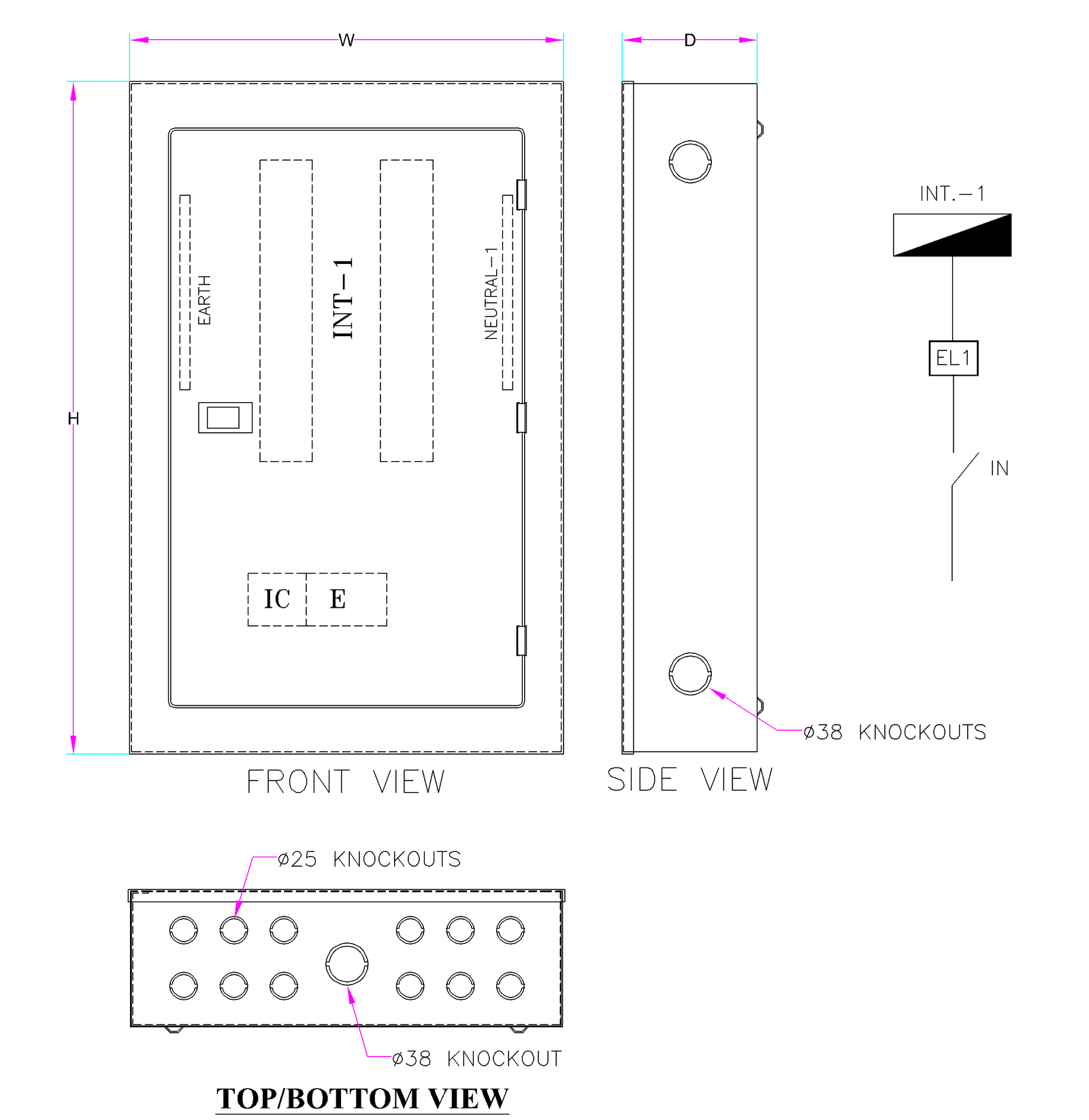
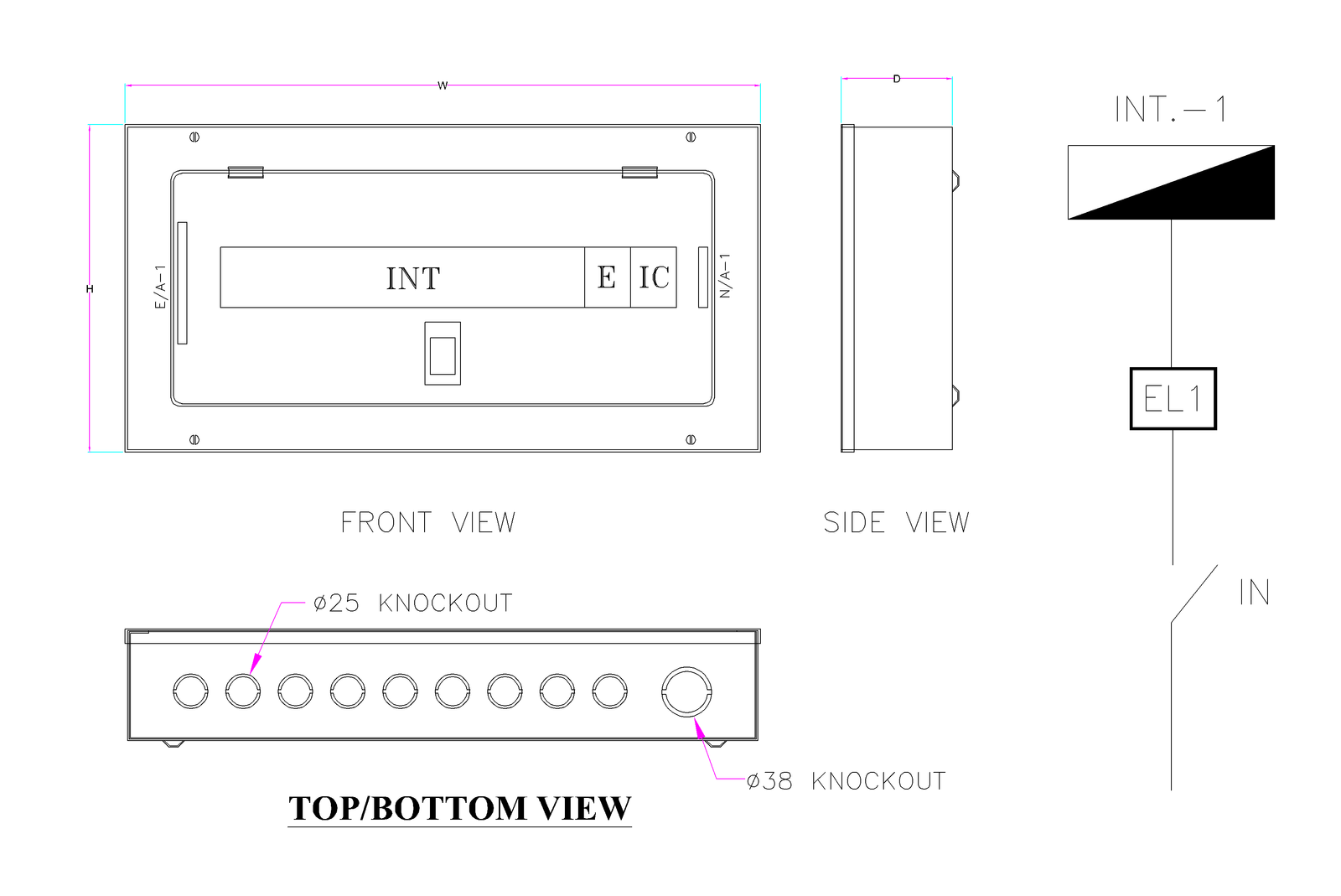
SPECIFICATIONS:
- Fabricated from 1.2mm steel sheet.
- Pre treated with chemical before powder coating.
- Hinged door with sliding lock.
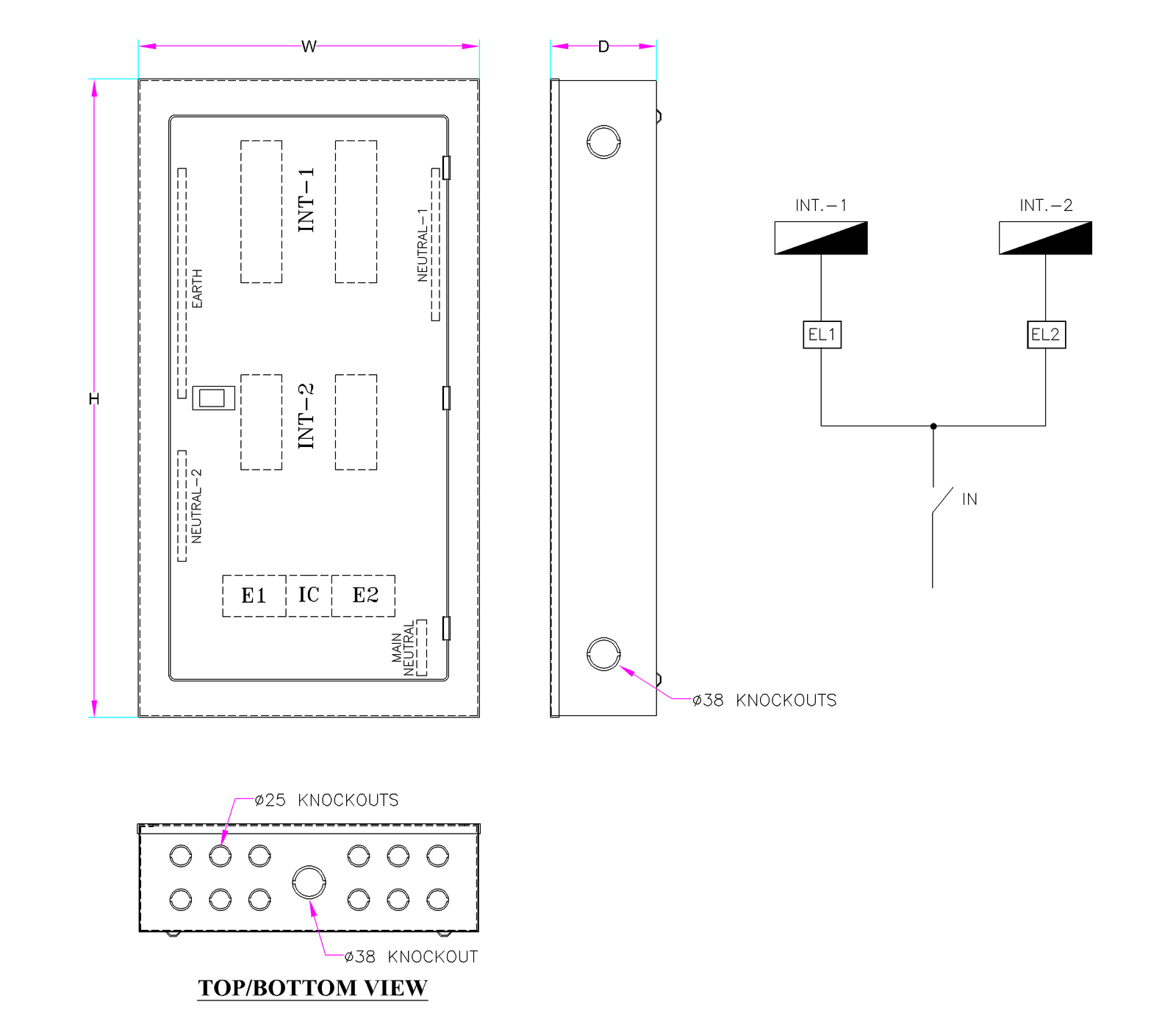
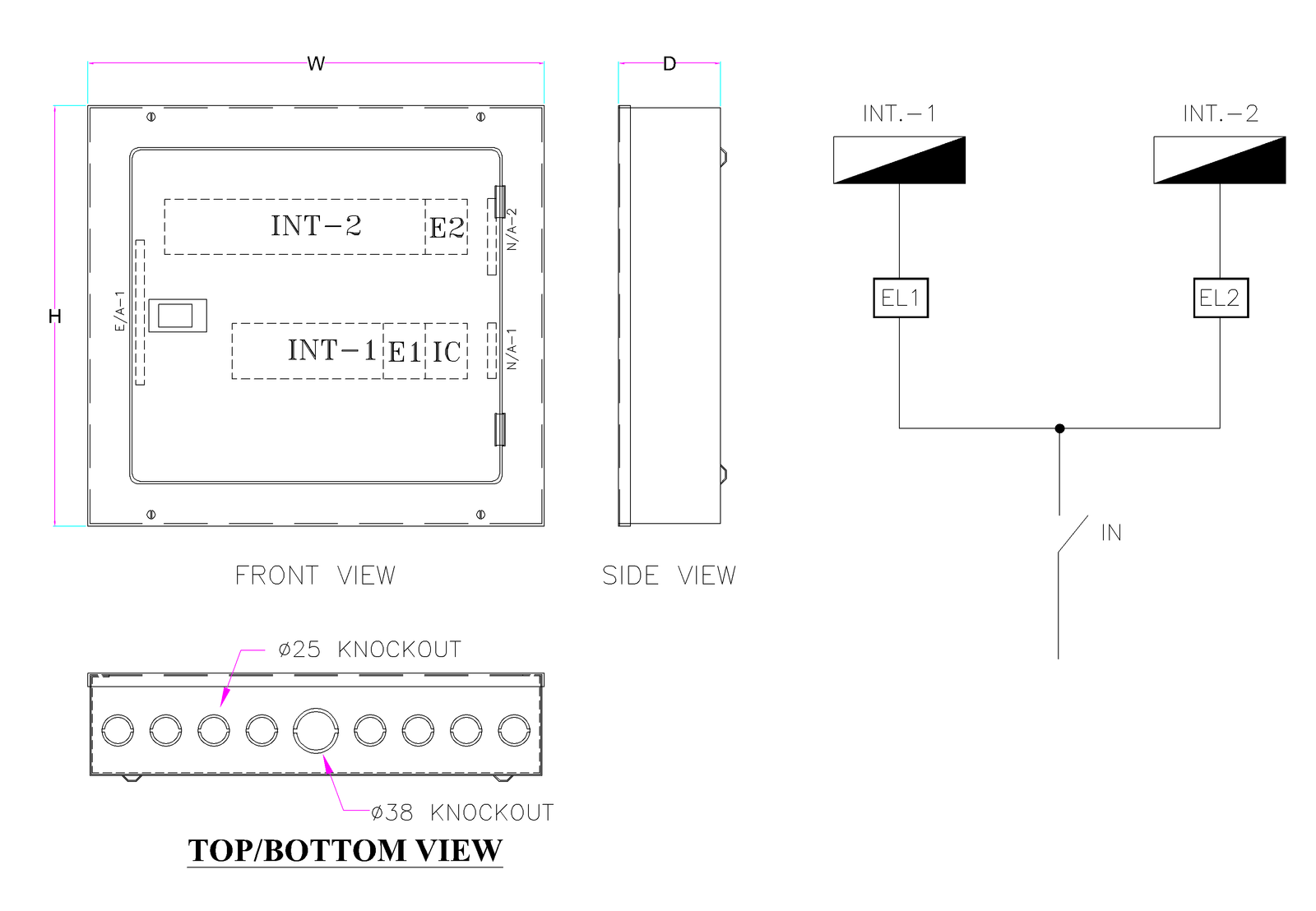
- Enclosure with Knockouts at Top, Bottom and both Sides for cable entry.
- Available in Flush and Surface type.
- Powder coated with Standard color RAL 7035. any other color on request with cost impact.
- Power Supply:
1. For TPN DB – 3 Phase +N, 415V, AC, 50HZ.
2. For SPN DB- Phase +N, 230V, Ac, 50HZ - MCBs 1P, 3P Din Rail mounting Type.
- MCB Pan Assembly DB- Interior): Insulated, Tinned copper busbar 100A /125A / 160A.
- Easy for installation and cabling as the sufficient space provided inside the DB.
- IP Protection: IP 31
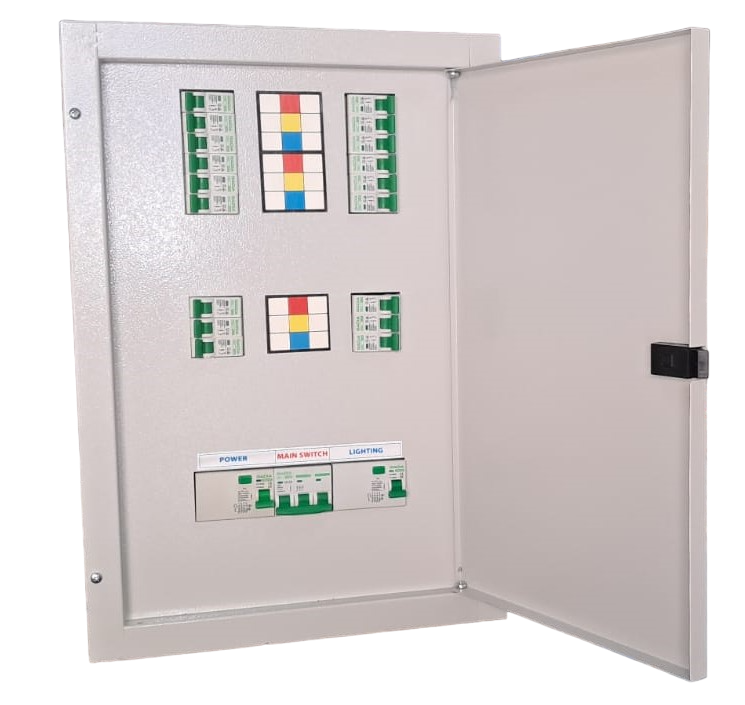
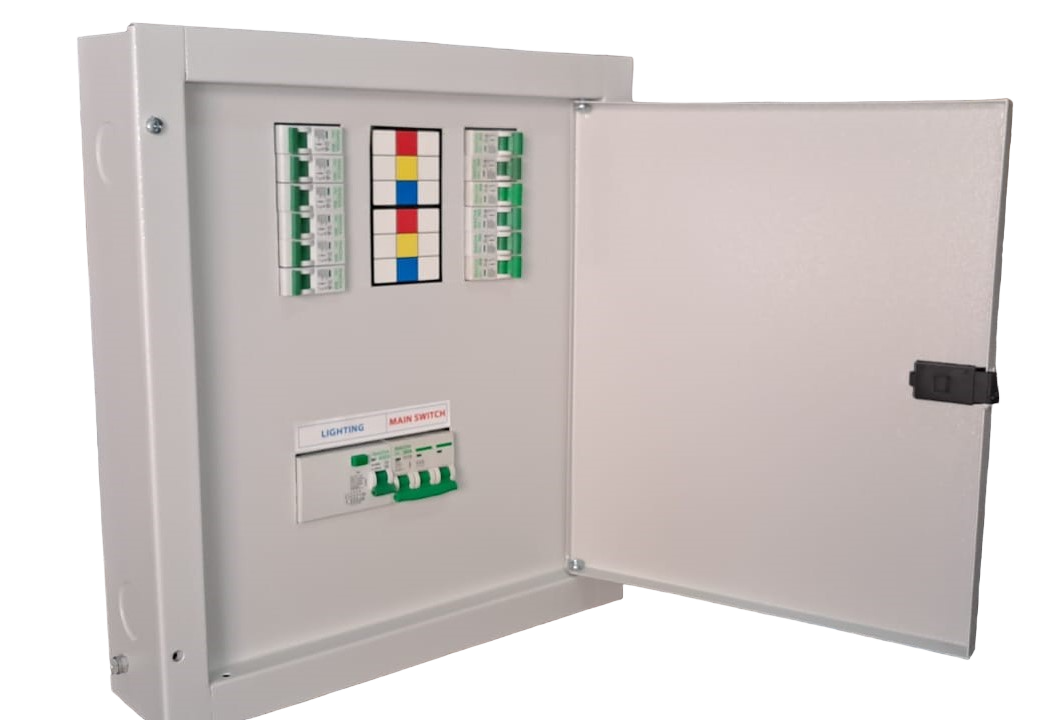


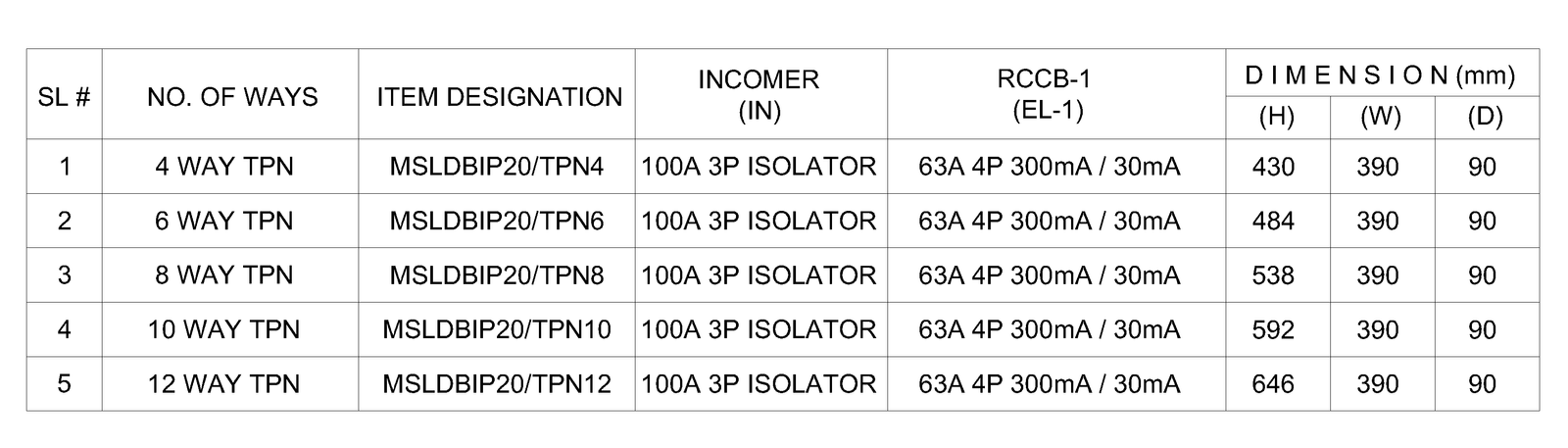
Non Split Type DB
TPN DB (Non Split)
SPN DB (Non Split)
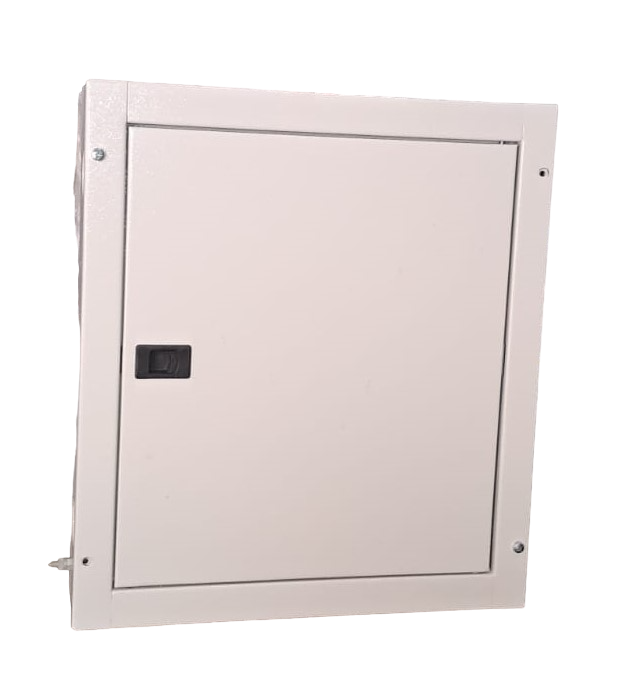
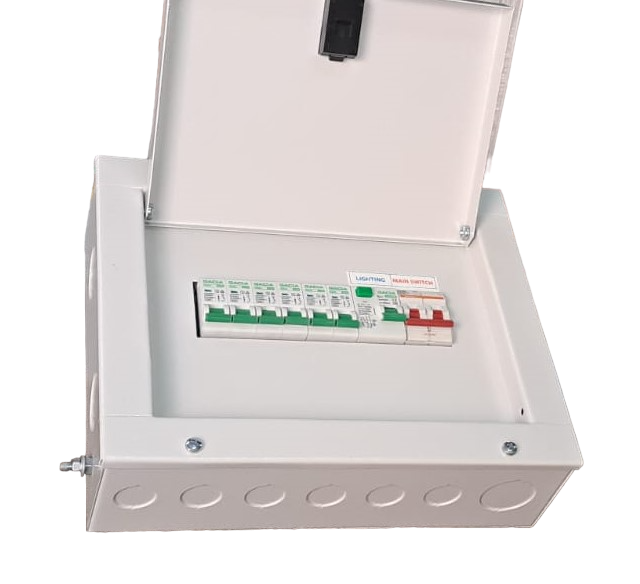
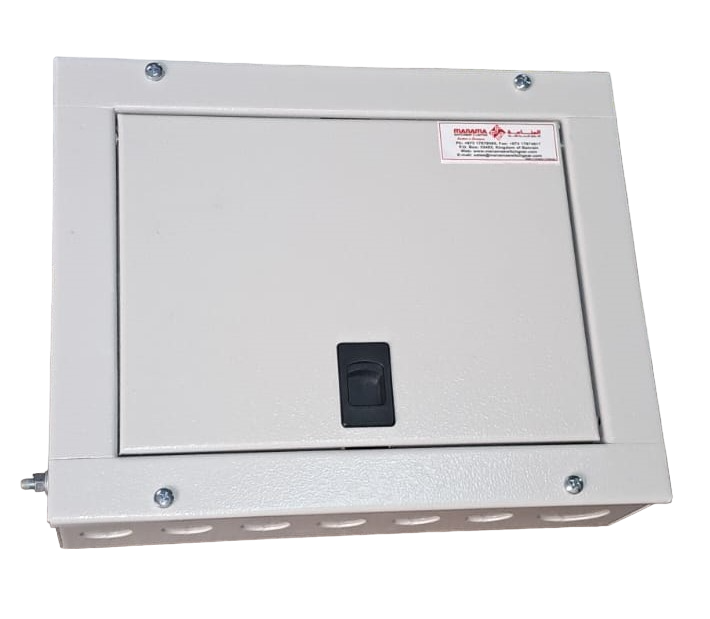
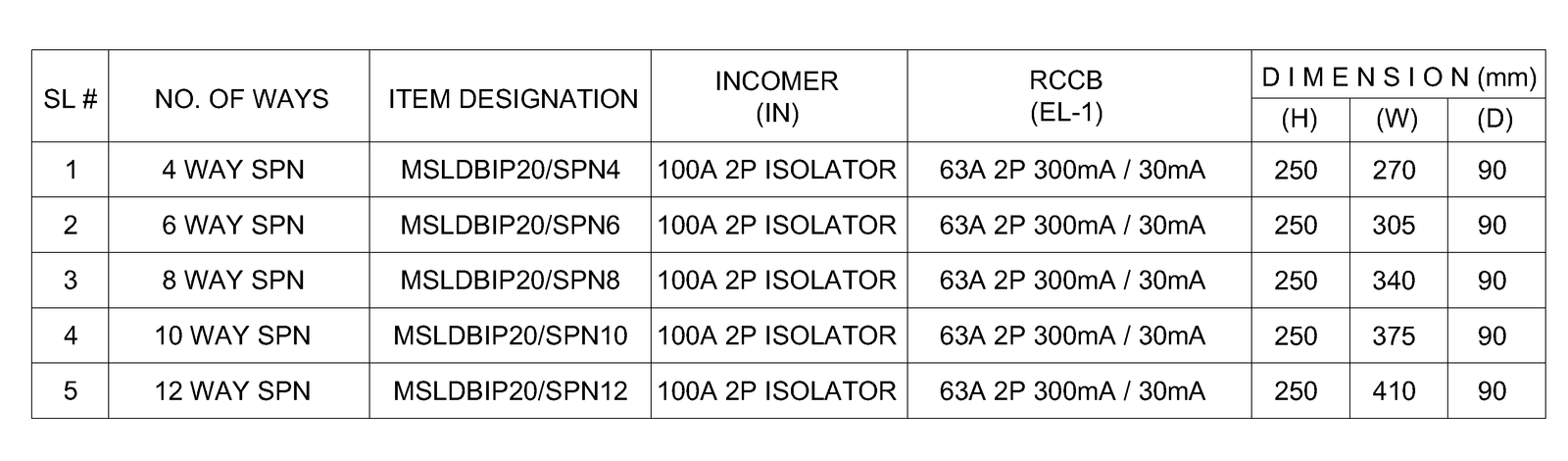




Split Type DB
TPN DB (Split)
SPN DB (Split)